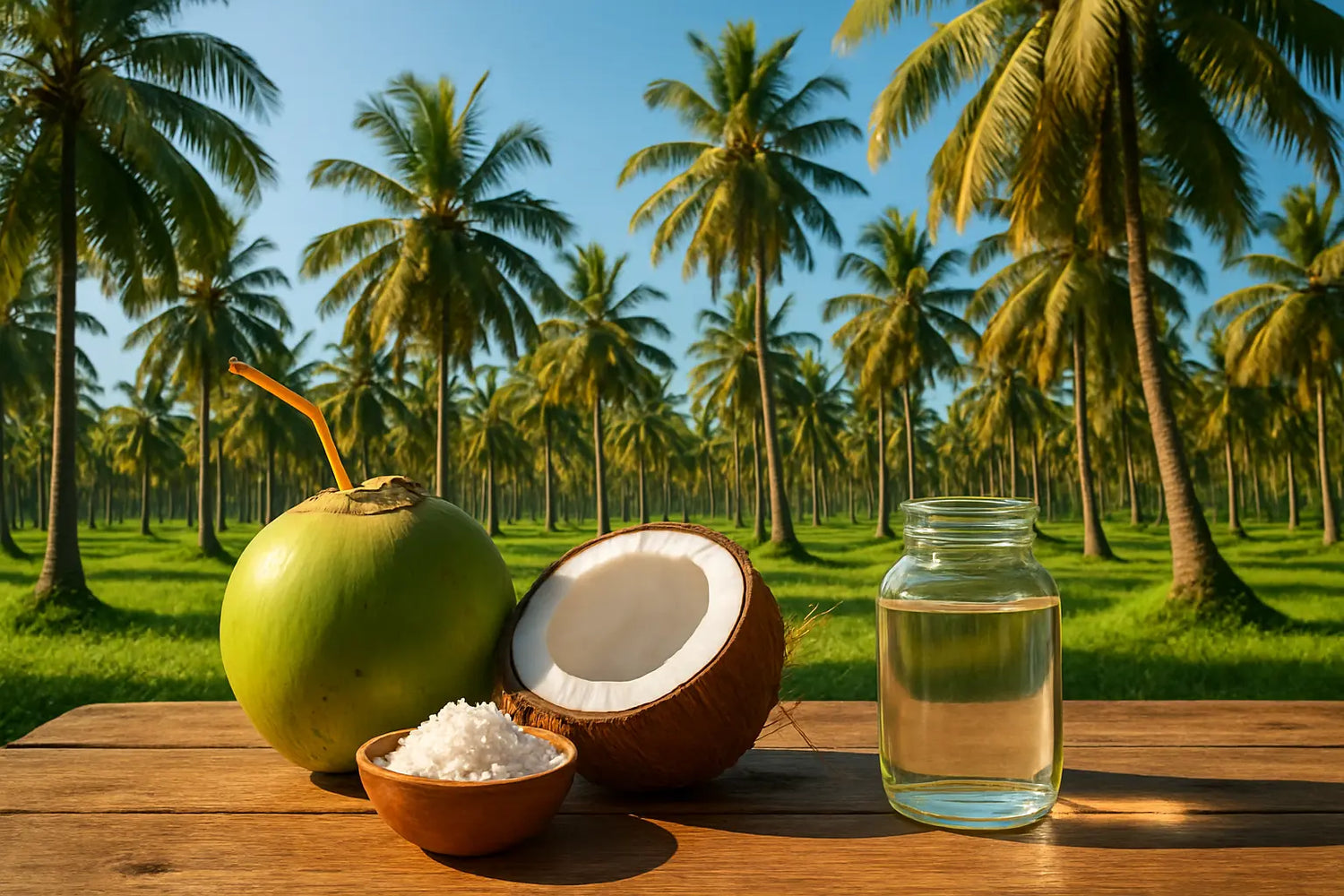
Imagine a sunny kitchen in Kerala. The air smells of spices and something sweet, nutty, and incredibly comforting. That’s the smell of coconut oil, or as many of us call it, nariyal oil. For generations, it's been the go-to for everything—from making crispy dosas to giving a champion head massage. But then, you hop online and see headlines screaming that it’s a health hazard, packed with bad fats. So, what’s the real story? Is this beloved oil a friend or a foe? Let's crack this coconut open and find out.
Table of Contents
- What's Actually Inside a Coconut?
- The Great Fat Debate: Why the Bad Rap?
- Ingredients Deep Dive: Not All Saturated Fats Are the Same
- Insights from the Web: The Quora Corner
- The Glowing Benefits of Coconut Oil
- Finding Balance: It’s Not Just About One Oil
- Frequently Asked Questions
What's Actually Inside a Coconut?
Before we talk about the oil, let’s talk about the source. The coconut is like a multi-purpose gift from nature. When it’s young and green, it gives us refreshing tender coconut water. As it matures, the white flesh inside, or the kernel, can be eaten fresh (grated coconut), dried to make desiccated coconut, or pressed to make coconut milk.
When this kernel is dried, it’s called copra. This is what is usually pressed to extract coconut oil. From a single coconut farm, we get everything from the fibrous husk of coconut (used to make ropes) to delicious treats like coconut jelly and nata de coco. It's a huge part of the coconut business for a reason!
The Great Fat Debate: Why the Bad Rap?
For decades, we were told to avoid saturated fats at all costs. Since coconut oil is about 90% saturated fat, it was automatically put on the “bad food” list. The concern was that saturated fats raise LDL (bad) cholesterol, which is linked to heart disease. This led to many people switching to other vegetable oils.
But here’s where the story gets interesting. The science on fat is evolving. We’re now learning that not all saturated fats behave the same way in our bodies. This is where we need to dive a little deeper into the ingredients.
Ingredients Deep Dive: Not All Saturated Fats Are the Same
The main reason coconut oil is different is because of its unique fatty acid profile. Most of the saturated fats in coconut oil are Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs).
- What are MCTs? Think of them as shorter, smaller fat molecules compared to the Long-Chain Triglycerides (LCTs) found in meat, dairy, and other vegetable oils.
- How do they work? Because they are shorter, your body digests MCTs differently. They go straight from the gut to the liver, where they are quickly used for energy or turned into ketones, which are like fuel for your brain. They are less likely to be stored as body fat.
- Lauric Acid: About 50% of the fat in coconut oil is a special MCT called lauric acid. It has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, meaning it can help fight off harmful bacteria and viruses. It also helps increase HDL (the 'good' cholesterol).
So, while coconut oil does raise LDL (bad) cholesterol, it also raises HDL (good) cholesterol, which is a very different picture from what we first thought.
Insights from the Web: The Quora Corner
People are buzzing with questions about coconut oil online. Let's look at what the community on Quora is saying and get some clarity.
-
Why was coconut oil considered bad, but now it's good?
The initial fear came from its high saturated fat content. However, as one user points out, traditional diets in places like Kerala also include a lot of fish, which is rich in Omega-3 fatty acids. This balance is crucial. The focus is shifting from vilifying one ingredient to understanding the whole dietary pattern. Read more on Quora.
-
How can Pacific Islanders eat a lot of coconut and have low heart disease?
Again, it's about the full picture. These populations traditionally ate whole foods—fresh coconut, fruits, tubers, and fish. Their lifestyles were also very active. Their overall diet was unprocessed and nutrient-dense, which offered protection that a single ingredient, viewed in isolation, cannot explain. See the discussion on Quora.
-
Is there a link between coconut oil and high cholesterol?
Yes, consuming coconut oil can raise cholesterol levels, including both LDL ('bad') and HDL ('good'). For this reason, people with existing high cholesterol or heart conditions should use it sparingly and talk to their doctor. Moderation is the key. Explore this on Quora.
The Glowing Benefits of Coconut Oil
Now for the fun part! Beyond the fat debate, coconut oil has some amazing practical uses that have stood the test of time.
- Coconut oil for hair growth: It's a classic for a reason. The lauric acid in coconut oil helps it penetrate the hair shaft, reducing protein loss and keeping it strong and moisturized. Brands like Parachute coconut oil and Kera coconut oil are household names for hair care. Using pure coconut oil for a weekly head massage can do wonders for shine and strength.
- Coconut oil for skin: It's a fantastic natural moisturizer. You can use virgin coconut oil for face cleansing or to soothe dry skin on your body. Its antimicrobial properties can also help with minor skin irritations.
- Coconut oil for cooking: Because it's stable at high temperatures, it's great for sautéing and frying. It adds a delicious, subtle flavour to dishes. Just be mindful of the portion size.
- Oil Pulling: Swishing a tablespoon of coconut oil in your mouth for 10-15 minutes (called oil pulling) is an ancient Ayurvedic practice believed to improve oral hygiene by killing harmful bacteria in the mouth.
Finding Balance: It’s Not Just About One Oil
The biggest lesson from the coconut oil story is that no single food is a magic bullet. A healthy body needs a variety of nutrients. While coconut oil has its place, your body also needs other types of fats, vitamins, and minerals to thrive.
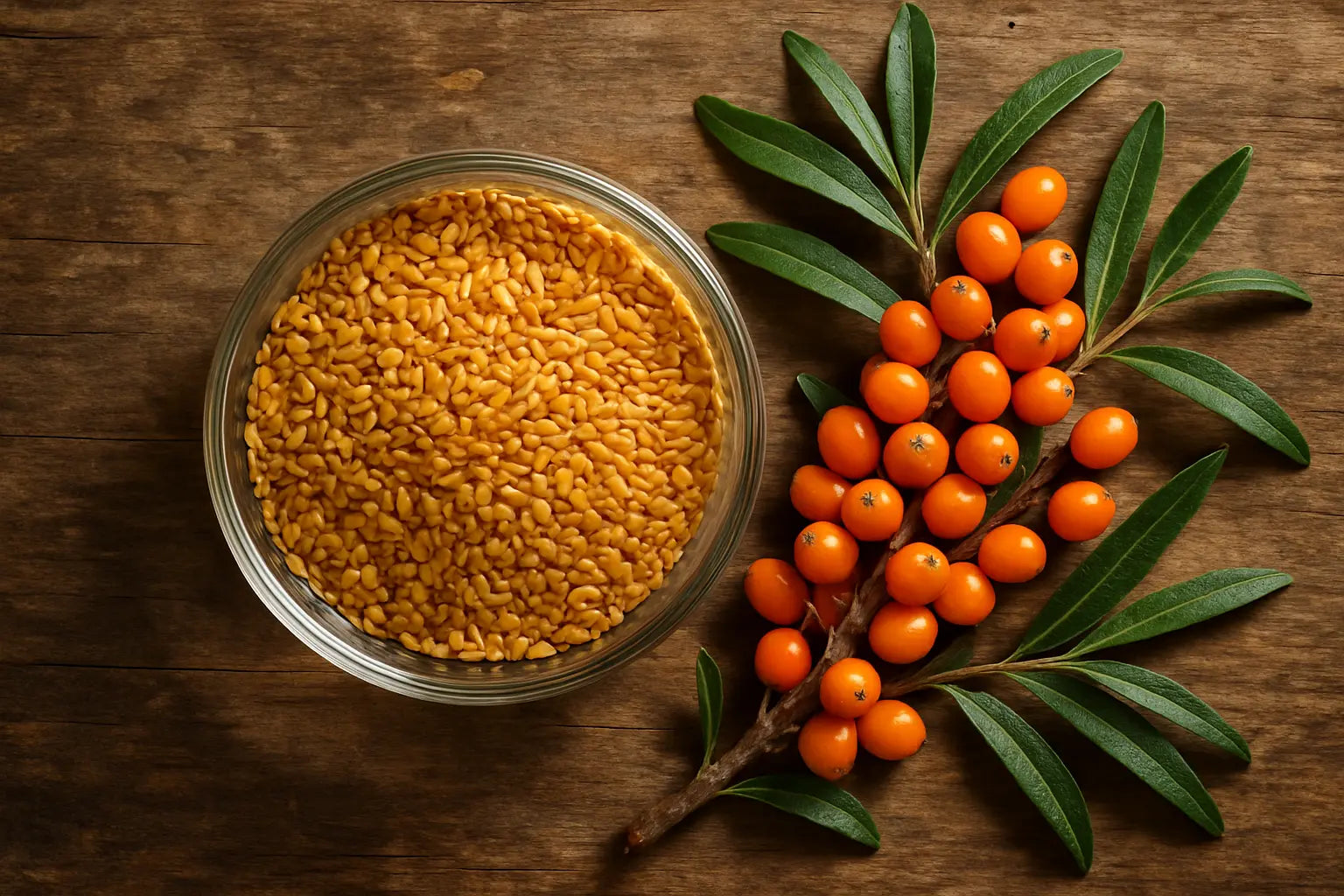
For example, while coconut oil provides some types of fatty acids, you also need a good balance of Omega-3, 6, and 9 for heart health and fighting inflammation. For skin health, the rare Omega-7 is a superstar. If you're looking to get that full spectrum of benefits for glowing skin and overall wellness, a supplement can be a great addition.
Daily All Day Sea Buckthorn Juice is packed with Omega 3, 6, 9, and the rare Omega 7. It’s a powerhouse for skin, boosting collagen and hydration from within. It supports your heart and immune system too, giving you a holistic health boost that one oil alone can't provide.
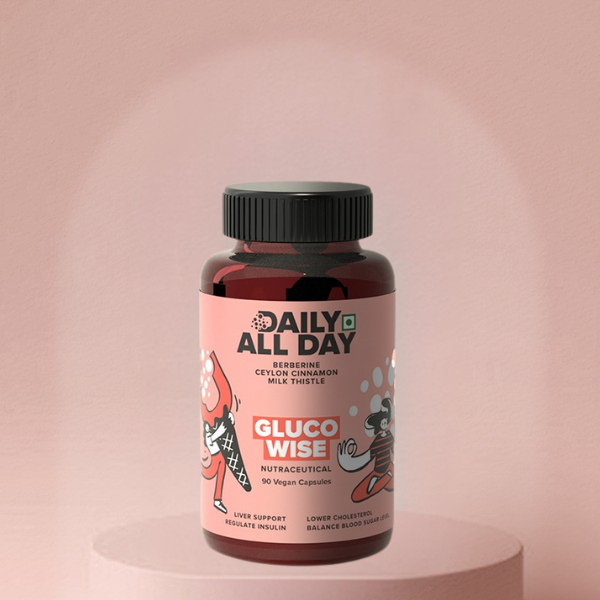
Similarly, if you're concerned about how your diet impacts your cholesterol and blood sugar, it's important to look beyond just the fats you consume. Managing your metabolic health requires a broader approach. A supplement like Daily All Day Gluco Wise is designed to help. With ingredients like Berberis Aristata and Ceylon Cinnamon, it supports healthy blood sugar and cholesterol levels, while Milk Thistle aids liver health. It’s a smart way to help your body maintain balance in today's world.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is the difference between virgin and regular coconut oil?
- Virgin coconut oil (often labelled as extra virgin coconut oil or cold pressed coconut oil) is made from fresh coconut meat. It's not refined or processed with chemicals, so it retains more nutrients and has a stronger coconut flavour and aroma. Refined coconut oil is made from dried copra, is typically bleached and deodorized, and has a more neutral taste.
- 2. Can I use coconut oil on my face every day?
- It depends on your skin type. For people with dry skin, it can be a great daily moisturizer. However, coconut oil is comedogenic, which means it can clog pores. If you have oily or acne-prone skin, it might cause breakouts. It's best to test it on a small area first.
- 3. How does coconut oil help hair?
- The molecular structure of coconut oil, especially its lauric acid content, allows it to penetrate the hair shaft better than many other oils. This helps prevent protein loss from the hair, which keeps it strong, reduces breakage, and helps it retain moisture, leading to less frizz and more shine.
- 4. Is coconut oil good for weight loss?
- The MCTs in coconut oil can slightly boost metabolism and increase feelings of fullness, which might help with weight management. However, it is still a high-calorie fat. Replacing other fats with coconut oil might have a small benefit, but simply adding it to your diet without cutting calories elsewhere will not lead to weight loss.
- 5. Is it really better to cook with coconut oil?
- Coconut oil has a high smoke point, especially the refined version, making it a stable choice for high-heat cooking like frying. Unlike some vegetable oils that can break down into harmful compounds at high temperatures, coconut oil holds up well. However, for everyday cooking, rotating it with other healthy oils like olive oil or mustard oil is a good practice for a balanced fatty acid intake. Just remember to check the health benefits of other cooking mediums as well.

The Final Verdict: Friend, Not Foe (In Moderation!)
So, what’s the final word on coconut oil? It’s not the villain it was once made out to be, but it’s also not a magical cure-all. The truth, as it often is, lies somewhere in the middle. The key is moderation and quality. Choosing virgin, cold-pressed coconut oil gives you more of the good stuff. Using it as part of a varied diet that includes other healthy fats is the smartest way to go.
The wisdom of places like Kerala isn't just about using coconut oil; it's about the entire lifestyle—a diet rich in fish, fresh vegetables, and whole foods. It’s about balance. And achieving that balance in our modern lives can sometimes use a little help.
To support your heart and metabolic health, especially when navigating dietary fats, consider a holistic approach. Products like Daily All Day Gluco Wise can be a great ally in managing cholesterol and blood sugar levels. And for that radiant skin and hair you're looking for, supplementing your diet with the rich omega fatty acids found in Daily All Day Sea Buckthorn Juice can provide the nourishment your body craves from the inside out. Ultimately, a healthy life is built on smart choices, balance, and listening to your body.